You can contact LEARNZ, part of CORE Education, at:
Postal Address:
PO Box 13 678,
Christchurch 8141,
New Zealand
A volcano is a landform made from magma erupting at the surface. Magma is molten rock within the earth. When magma erupts out of a volcano it is called lava.
The size and shape of a volcano depends on:
Volcanoes would not exist if the Earth’s surface was solid and did not move.
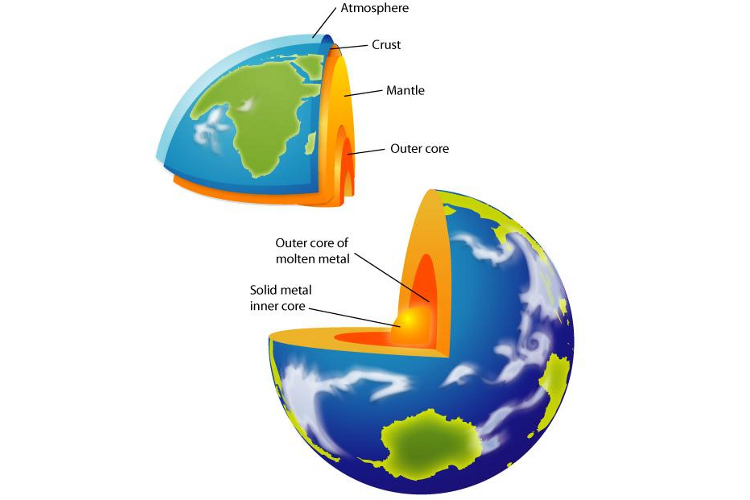
The Earth has five layers: the inner and outer core, the lower and upper mantle, and the crust. The deeper you go below the Earth’s crust, the hotter it gets.
The high temperatures (900°C) and high pressures in the mantle layer of the Earth are enough to melt rock. The high pressure changes the rock into a thick semisolid called magma. The hot molten rock in the mantle does not normally make it through the many kilometres of crust that forms the ground that we walk on. Only in certain areas where there are cracks or breaks in the crust, such as at plate boundaries, can the molten mantle start to creep through.
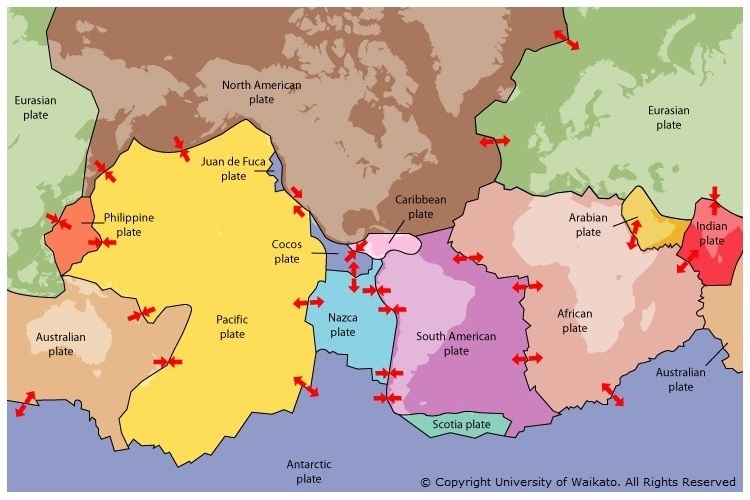 Plate tectonics
Plate tectonicsOn the Earth today there are six large plates and many smaller ones. The plates move in slow motion and are always changing shape. It is thought that convection currents in the mantle of the Earth form the energy to move the tectonic plates from a few millimetres to a maximum of about 15cm per year.
At the edge of the tectonic plates there are three types of movement:
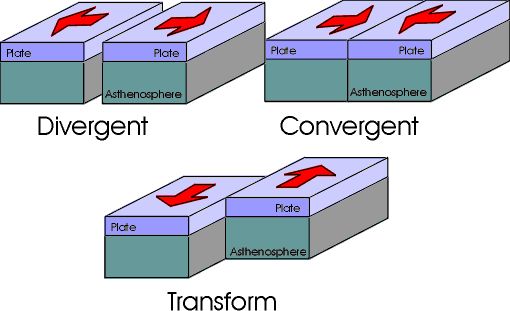
 Plate Tectonics in Aotearoa
Plate Tectonics in AotearoaAotearoa New Zealand sits on the edge of two tectonic plates, the Indo-Australian and the Pacific plates. This makes Aotearoa geologically active with many earthquakes, geothermal areas and volcanoes.
Complete the Volcanic activity quiz
> Discover more about volcanoes and volcanic hazards